Table of Contents
- What Is Agentic AI? Architecture, MCP, and Real-World Use Cases (2026)
What Is Agentic AI? Architecture, MCP, and Real-World Use Cases (2026)
Agentic AI represents the next evolutionary step in artificial intelligence systems. Unlike traditional AI models or chat-based LLMs that merely respond to prompts, Agentic AI systems can autonomously plan, decide, act, evaluate outcomes, and iterate toward a defined goal.
By 2026, Agentic AI has become the architectural foundation behind modern AI agents, autonomous workflows, and production frameworks such as LangGraph, CrewAI, AutoGen, and the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
This article is designed as a technical, authority-grade reference for developers, AI engineers, architects, and decision-makers seeking a system-level understanding of Agentic AI.
Related reading: If you are looking for curated learning paths, comparisons, and recommendations, see our in-depth guide on Best Udemy Agentic AI Courses for 2026.
Agentic AI vs Traditional AI Systems
Traditional AI systems operate in a reactive paradigm. They respond to user input but do not independently pursue objectives. Agentic AI, by contrast, operates in a continuous goal-driven loop.
| Aspect | Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction model | Prompt → Response | Goal → Plan → Act → Evaluate |
| Autonomy | None | High |
| Memory | Stateless or short context | Persistent short- and long-term memory |
| Reasoning | Single-step | Multi-step planning and execution |
| Tool usage | Optional | Core capability |
A chatbot answers questions. An Agentic AI system solves problems over time.
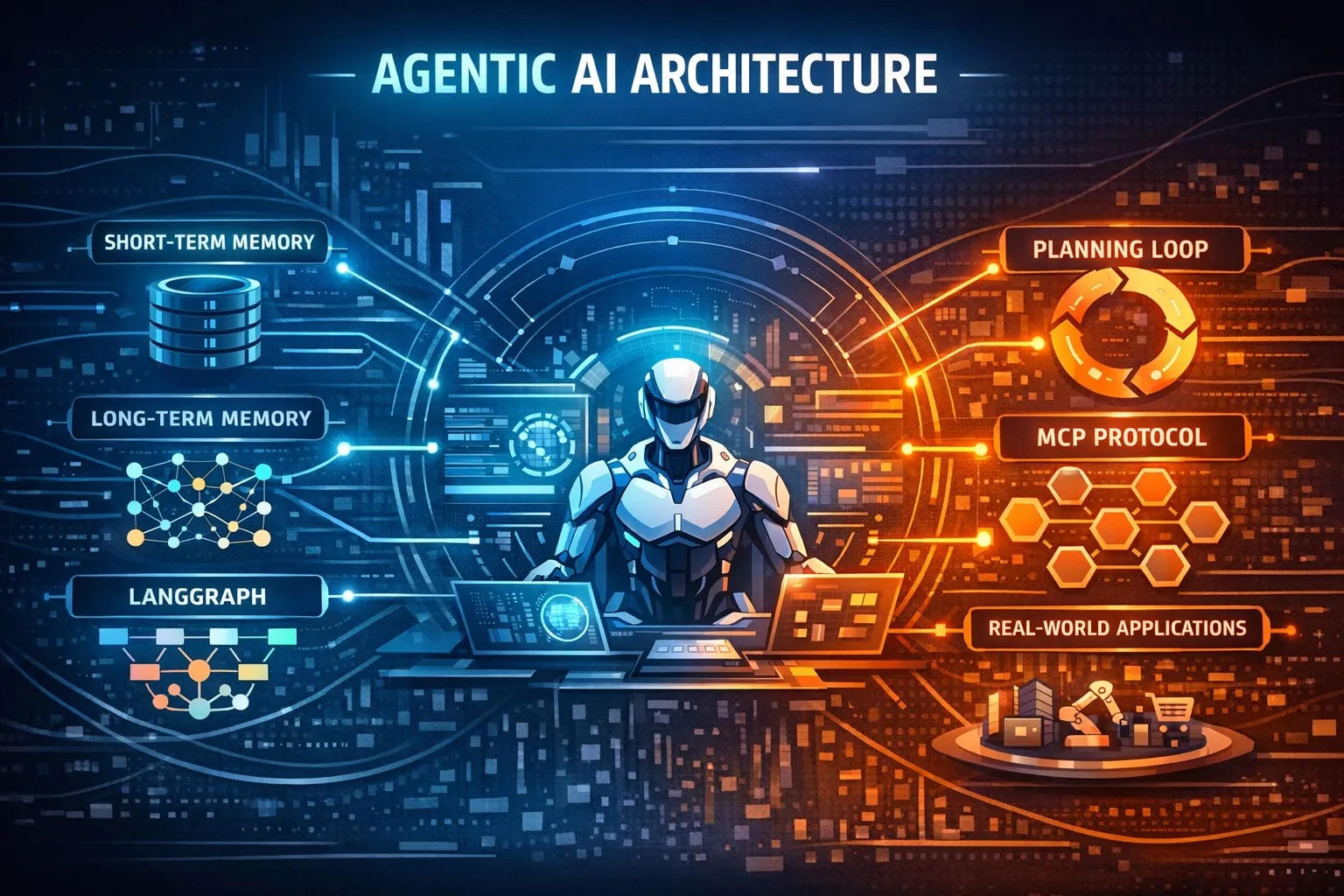
Core Architecture of Agentic AI
Most production-ready Agentic AI systems share five core architectural layers.
Goal Definition and Task Decomposition
Every Agentic AI system begins with a high-level objective. This objective is decomposed into smaller, executable tasks that can be planned, executed, and evaluated independently.
Task decomposition is essential. Without it, autonomous reasoning degrades into linear prompt execution.
Planning and Decision Engine
The planning layer determines what actions to take, in what order, and under which conditions. Modern Agentic AI systems employ multi-step reasoning strategies and graph-based execution models.
Frameworks such as LangGraph model agent workflows as state machines, enabling conditional branching, retries, error handling, and parallel execution.
Action and Tool Invocation Layer
Agentic AI systems interact with the external world through tools. These may include APIs, databases, code execution environments, file systems, and third-party services.
This layer converts reasoning outputs into real operational behavior.
Memory and State Management
Memory is a defining characteristic of Agentic AI. Most systems implement:
- Short-term memory for active task context
- Long-term memory using vector databases or structured knowledge stores
Memory enables learning from prior executions, continuity across sessions, and long-running autonomous behavior.
Evaluation and Self-Reflection
After executing an action, the agent evaluates the outcome. If the result does not advance the goal, the system revises its plan and continues execution.
This feedback loop enables self-correction and continuous improvement.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Explained
For a deeper hands-on perspective, you can also explore official documentation and community resources:
- LangGraph Documentation
- CrewAI Framework
- AutoGen by Microsoft
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) Specification
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) defines a standardized interface for how AI agents access tools, memory, and external resources. MCP cleanly separates reasoning models from execution environments.
In Agentic AI architectures, MCP enables secure tool exposure, consistent context passing, and scalable interoperability across agents and services.
Single-Agent vs Multi-Agent Systems
Agentic AI systems can be implemented using either single-agent or multi-agent architectures.
Single-Agent Systems
Single-agent systems handle planning, execution, and evaluation within one agent. They are simpler to design and well-suited for bounded or deterministic tasks.
Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems assign specialized roles to multiple agents. Agents collaborate, exchange context, and coordinate actions to solve complex objectives.
CrewAI emphasizes role-based collaboration, while AutoGen focuses on structured agent-to-agent communication.
Real-World Use Cases of Agentic AI in 2026
Agentic AI is actively deployed in production across multiple industries.
Autonomous Research Agents
Used for market research, competitive intelligence, and large-scale literature reviews.
Software Engineering Agents
Assist with code generation, testing, debugging, refactoring, and CI/CD automation.
Data and Analytics Agents
Automate data ingestion, insight generation, anomaly detection, and reporting pipelines.
Business Process Automation
Power autonomous workflows in customer support, CRM systems, and operational optimization.
Risks, Limitations, and Guardrails
Despite its power, Agentic AI introduces new risks, including hallucinated actions, infinite execution loops, tool misuse, and security vulnerabilities.
Production-grade systems must implement:
- Rate limits and execution caps
- Human-in-the-loop approvals
- Sandboxed execution environments
- Comprehensive audit logging
Without governance, autonomous systems are unsuitable for real-world deployment.
Why Agentic AI Matters
Agentic AI marks a shift from assistive AI to autonomous systems. This transition fundamentally changes how software is built, how work is automated, and how humans collaborate with machines.
Understanding Agentic AI is now a core competency for modern AI practitioners.
Conclusion
For readers interested in practical learning paths and course comparisons, this article connects directly to our money page:
This internal linkage helps bridge foundational knowledge with actionable next steps.
Agentic AI is not a buzzword. It is an architectural paradigm defining how intelligent systems are built in 2026. By combining planning, memory, tool usage, and self-evaluation, Agentic AI enables machines to operate autonomously in complex environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is an AI architecture in which systems autonomously plan, act, evaluate results, and iterate toward a defined goal using memory and tools.
Is Agentic AI production-ready in 2026?
Yes. Frameworks such as LangGraph, CrewAI, AutoGen, and MCP are actively used in production environments.
What is MCP in Agentic AI?
MCP (Model Context Protocol) standardizes how AI agents securely access tools, memory, and external services.
Do Agentic AI systems require multiple agents?
No. Agentic behavior can be implemented with a single agent, although multi-agent systems offer greater scalability and specialization.